
Amazon EC2起動時にユーザーデータで任意のSSHポートに変更する
はじめに
sshd が LISTEN するデフォルトポートは、Port#22 ですが 今回は、Port#2222 に変更してみたいと思います。
利用する AMI は、以下のとおりです。
- Amazon Linux AMI 2017.03.0 (HVM), SSD Volume Type - ami-923d12f5
- Ubuntu Server 16.04 LTS (HVM), SSD Volume Type - ami-afb09dc8
- CoreOS-stable-1353.7.0-hvm - ami-8284aee5
では、それぞれの方法について見ていきます。
Amazon Linux 環境の場合
ユーザーデータ入力時に「テキストで」を選択し、以下のシェルスクリプトを入力します。
#!/bin/sh -ex /bin/sed -i -e 's/^#Port 22$/Port 2222/' /etc/ssh/sshd_config service sshd restart
なお、セキュリティグループの設定時に、カスタムTCPルールとして TCP 2222 の開放をお忘れなく
SSH クライアントから接続する際は、ポート 2222 を指定します。
~ $ ssh [email protected] -p 2222 : __| __|_ ) _| ( / Amazon Linux AMI ___|\___|___| https://aws.amazon.com/amazon-linux-ami/2017.03-release-notes/ 6 package(s) needed for security, out of 6 available Run "sudo yum update" to apply all updates. [ec2-user@ip-172-31-31-136 ~]$ sudo netstat -anp | egrep '2222|Local Address' Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:2222 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 2664/sshd tcp 0 36 172.31.31.136:2222 124.219.179.165:62787 ESTABLISHED 2707/sshd tcp 0 0 :::2222 :::* LISTEN 2664/sshd [ec2-user@ip-172-31-31-136 ~]$
Port#2222 で接続出来ましたね。
Ubuntu Server 16.04 LTS 環境の場合
ユーザーデータ入力時に「テキストで」を選択し、以下のシェルスクリプトを入力します。
#!/bin/sh -ex /bin/sed -i -e "s/Port 22/Port 2222/" /etc/ssh/sshd_config systemctl restart ssh
Amazon Linux 同様、SSH クライアントから接続する際にポート 2222 を指定します。
~ $ ssh [email protected] -p 2222 : Welcome to Ubuntu 16.04.2 LTS (GNU/Linux 4.4.0-1013-aws x86_64) * Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com * Management: https://landscape.canonical.com * Support: https://ubuntu.com/advantage Get cloud support with Ubuntu Advantage Cloud Guest: http://www.ubuntu.com/business/services/cloud 0 packages can be updated. 0 updates are security updates. The programs included with the Ubuntu system are free software; the exact distribution terms for each program are described in the individual files in /usr/share/doc/*/copyright. Ubuntu comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by applicable law. To run a command as administrator (user "root"), use "sudo <command></command>". <command></command>See "man sudo_root" for details. ubuntu@ip-172-31-30-164:~$ sudo netstat -anp | egrep '2222|Local Address' Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:2222 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1319/sshd tcp 0 36 172.31.30.164:2222 124.219.179.165:62492 ESTABLISHED 1339/sshd: ubuntu [ tcp6 0 0 :::2222 :::* LISTEN 1319/sshd ubuntu@ip-172-31-30-164:~$
問題なく、接続出来ました。
CoreOS 環境の場合
CoreOS に関しては、Amazon Linux や Ubuntu Server 16.04 LTS とはお作法が少し異なります。 予め以下の ignition.conf ファイルを作成しておいてください。
{
"ignition": { "version": "2.0.0" },
"systemd": {
"units": [{
"name": "sshd.socket",
"enable": true,
"contents": "[Socket]\nListenStream=2222\nFreeBind=true\nAccept=yes\n[Install]\nWantedBy=multi-user.target"
}]
}
}
詳細については、以下のドキュメントをご参照ください。
Amazon Linux や Ubuntu Server 16.04 LTS 環境では、 ユーザーデータ入力時に「テキストで」を選択しておりましたが、CoreOS 環境では 「ファイルとして」を選択し、先程作成頂いた ignition.conf ファイルを選択します。
イメージは、下記のとおりです。
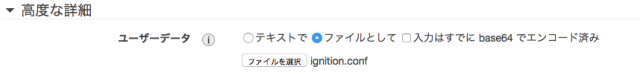
その他の手順については、Amazon Linux や Ubuntu Server 16.04 LTS 環境と同様に EC2 インスタンスを起動してください。
では、SSH での接続確認を実施します。
~ $ ssh [email protected] -p 2222 : Container Linux by CoreOS stable (1353.7.0) core@ip-172-31-22-20 ~ $ sudo netstat -anp | egrep '2222|Local Address' Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name tcp6 0 0 :::2222 :::* LISTEN 1/systemd tcp6 0 0 172.31.22.20:2222 124.219.179.165:62412 ESTABLISHED 1/systemd core@ip-172-31-22-20 ~ $
CoreOS も接続出来ました。
最後に
sshd のデフォルトポートを変更することで、多少なりとも セキュリティ向上に寄与出来るのではないかと思われます。 ただし、セキュリティグループのインバウンドは TCP 22 ではなく カスタムTCPルール(今回の場合、TCP 2222)を開放する必要があります。 この点について、ご注意ください。
ではでは








